Septic
tank: Provided in areas where sewer have not been laid and for isolated
communities, schools,hospitals, other public institution etc.
- It is a sedimentation tank with longer detention time i.e. 12 to 36 hours
- Both sedimentation and sludge digestion takes place in this tank.
- Effluents should be disposed off either for sub surface irrigation or in cess pools or soak pits or treated inlet in trickling filter before disposed off in water course
- Sludge collected at the bottom gets digested anaerobically. The digested sludge is periodically removed.
Design
Criteria:
- Capacity of tank = sewage stored in detention time + volume of sludge stored during period of cleaning
- Sludge: 30 lit/person/year
- Period of clearing 6 months to 3 years (generally 1 year)
- Detention time: 12 to 36 hours (generally 24 hours)
Disposal
of effluents from septic tank: The
effluent of septic tank will have BOD of 100
to 200 mg/I and hence it can not disposed
of into water courses.
Method of Septic tank effluent disposal:
- Absorption trenches
- Soak pit
- Leaching cess Pool
Sub Surface irrigation Using Absorption
trenches: The suspended organic matter
present in the effluent will be absorbed in the absorption trench filled with gravel
Soak pit: The effluent is allowed to be soaked or absorbed into the surrounding soil. Pit is filled with xave1 brick bats etc
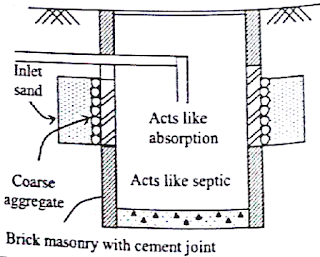
Cess pool: The top portion acts a absorption trench and bottom portion acts as a Septic
tank
used when subsoil is porous and when there is no well nearby.
- Incoming sludge is not allowed to get mixed up with sludge Suitable for small treatment plants where separate sedimentation tank and sludge digestion tank can not be constructed
- Depth of tank is more, costlier construction
- Obsolete these days
- Its is a anaerobic unit
- The upper chamber is used for sedimentation of solid-s and the lower chamber is meant for digestion and storage.




No comments:
Post a Comment